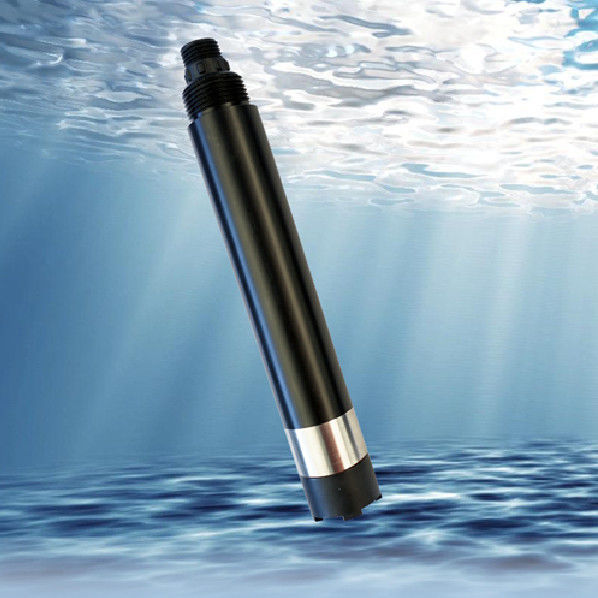
KFDO310 integrated on-line fluorescence dissolved oxygen sensor is designed and made based on the quenching principle of excited fluorescence of specific substances in physics. The blue light from the light-emitting diode illuminates the fluorescent material on the inner surface of the fluorescent cap. The fluorescent material on the inner surface is excited and emits red light. By detecting the phase difference between the red light and the blue light, and comparing it with the internal calibration value, the concentration of oxygen molecule can be calculated, and the final value can be output by temperature automatic compensation.
No electrolytes, no polarization
No need to consume oxygen, not affected by the flow rate
Built-in temperature sensor, automatic temperature compensation
Free from chemicals like sulfides
Small drift, fast response, more accurate measurement
Maintenance-free, long service life, lower use cost
Fluorescent caps are easy to replace
RS-485 interface, Modbus-RTU protocol
| Model number |
KFDO310 |
| Measuring principle |
fluorescence |
| Range |
0ー20 mg/L (0ー200% saturation, 25 °C) |
| Resolution |
0.01 mg/l, 0.1 °C |
| Precision |
± 2% f.s. , ± 0.5 °C |
| Temperature compensation |
Automatic temperature compensation (PT1000) |
| Output mode |
RS-485 bus, Modbus-RTU protocol |
| Working conditions |
0ー45 °C, < 0.2 mpa |
| Storage temperature |
- 5 ~ 65 °C |
| Installation mode |
Immersion mounting |
| Cable length |
5 meters, other length can be customized |
| Power consumption |
< 0.05 W |
| Power supply |
12 ~ 24 VDC ± 10% |
| Protection level |
IP68 |
| Calibration |
Two-point calibration |
| Fluorescent cap life |
Guaranteed Use for one year (under normal use) |
| Material for sensor housing |
Pom and 316L stainless steel |


The temperature sensing part should be immersed below the liquid surface to avoid collision with the film head surface. The head part of the membrane should be free from sediment.
Tips:Dissolved Oxygen from Photosynthesis

Dissolved oxygen can enter the water as a byproduct of photosynthesis.
While most photosynthesis takes place at the surface (by shallow water plants and algae), a large portion of the process takes place underwater (by seaweed, sub-surface algae and phytoplankton). Light can penetrate water, though the depth that it can reach varies due to dissolved solids and other light-scattering elements present in the water. Depth also affects the wavelengths available to plants, with red being absorbed quickly and blue light being visible past 100 m. In clear water, there is no longer enough light for photosynthesis to occur beyond 200 m, and aquatic plants no longer grow.In turbid water, this photic (light-penetrating) zone is often much shallower.
Regardless of wavelengths available, the cycle doesn’t change. In addition to the needed light, CO2 is readily absorbed by water (it’s about 200 times more soluble than oxygen) and the oxygen produced as a byproduct remains dissolved in water¹⁰. The basic reaction of aquatic photosynthesis remains:
CO2 + H2O → (CH2O) + O2
As aquatic photosynthesis is light-dependent, the dissolved oxygen produced will peak during daylight hours and decline at night.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 


